Blockchain, cryptocurrencies and their applications
In recent years, blockchain and cryptocurrency technologies have attracted a great deal of attention in Nigeria, both among entrepreneurs and ordinary citizens. As the largest economy in Africa, Nigeria has seen a rapid growth in interest in these innovative technologies, and many see the potential for them to change traditional financial models and support the country’s economic development.
What is blockchain?
Blockchain, a distributed database, is a digital technology that allows data to be stored and transmitted without intermediate intermediaries, providing transparency, security and immutability of information.
How does blockchain technology work?
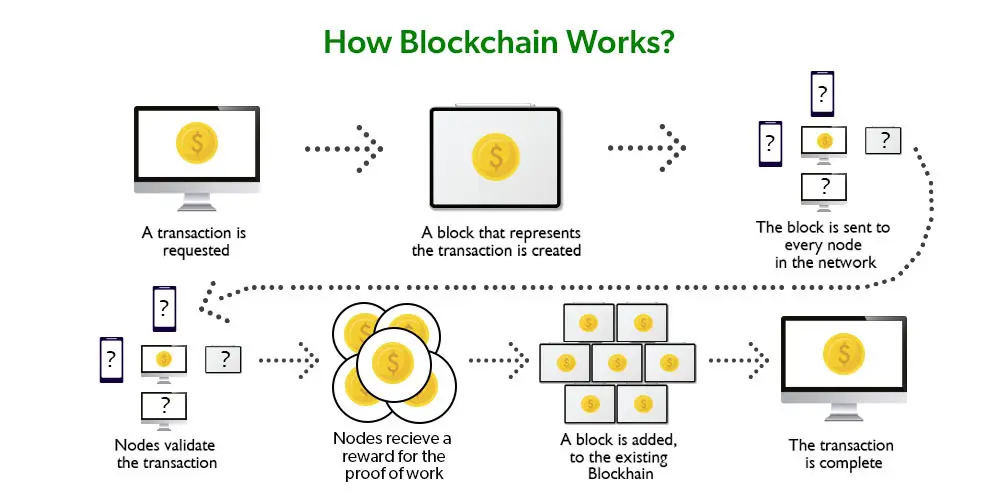
The basic principle of how blockchain works is that data is written into blocks, which are then linked together to form a chain of blocks (hence the name “blockchain”).
Here’s how it works in more detail:
- Decentralization: Unlike centralized systems where data is stored on a central server, blockchain uses a decentralized network of nodes (computers), each containing a complete copy of the blockchain. This ensures the reliability and security of the data, as changing information requires the consent of the majority of nodes in the network.
- Hashing and cryptography: Each block in the blockchain contains a unique hash code that is formed based on the data in the block and the hash of the previous block. This ensures communication between blocks and prevents the possibility of altering data in past blocks. In addition, blockchain uses cryptographic methods to protect information and authenticate transactions.
- Consensus protocols: To add new blocks to the blockchain, the blockchain uses consensus protocols, which define rules and procedures for agreement among network participants. For example, cryptocurrency networks such as Bitcoin use the Proof of Work protocol, while other blockchains may use Proof of Stake or other algorithms.
- Data immutability: Each block contains a hash of the previous block, making its contents immutable. If even one node in the network tries to change the data in a block, it will change its hash and break the integrity of the entire chain. Since changing the hash of a previous block will affect all subsequent blocks, such data manipulation attempts become difficult and easily detectable.
Blockchain in Nigeria:
In Nigeria, blockchain is finding applications in various fields:
Financial Services:
Blockchain is bringing revolutionary changes to financial services, making them more accessible and cheaper for the public. Decentralized Financial Systems (DeFi) open up opportunities for transactions without having to go to traditional banks. Cryptocurrencies are becoming an alternative means of payment and savings, and blockchain is increasing the transparency and efficiency of financial markets.
Public Administration:
Blockchain adoption in public administration can improve voting processes, supply chain management and other government functions. This improves transparency and efficiency in government operations, and helps in the fight against corruption.
Business:
In business, blockchain is helping to increase transparency and efficiency in supply chains, which can reduce costs and increase profits for companies. In addition, blockchain can stimulate the creation of new products and services.
Education:
Blockchain is being used to store diplomas and certificates, making this information secure and accessible. The technology also enables the creation of decentralized educational platforms.
Healthcare:
In healthcare, blockchain is used to store medical records, ensuring privacy and accessibility of information. The technology also facilitates the creation of decentralized healthcare systems.
Agriculture:
Blockchain enables traceability of food origins, increasing supply chain transparency and ensuring product safety. The technology is also being used to create decentralized agricultural finance systems.
Cryptocurrencies and their acceptance in Nigeria

Is cryptocurrency allowed in Nigeria?
The status of cryptocurrencies in Nigeria is variable and subject to change.
The Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN) banned the use of cryptocurrencies as legal tender in 2021.
However, the CBN has not banned the possession or trading of cryptocurrency.The regulator said it is working to establish a legal framework to regulate the cryptocurrency market.
The Nigerian government eventually lifted the ban on cryptocurrency in December 2023, effectively making them legal within the country. However, the situation may change depending on the decisions of the regulators and the government.
Which cryptocurrency is most commonly used in Nigeria?
Nigerians have shown a huge interest in cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, Etherium and other altcoins. This interest can be attributed to several factors:
Financial Inclusion: Many Nigerians, especially the younger generation, are looking for alternative ways to invest and store their money, especially in the face of economic instability and high inflation.
Money Transfers: Thanks to cryptocurrencies, many Nigerians can send and receive money from abroad quickly and with minimal fees, bypassing traditional financial intermediaries.
Investing and trading: For many Nigerians, cryptocurrencies have become a target for investment and trading on stock exchanges, where they see the potential for profits amid rapid price increases.
Conclusion
Despite the growing interest in blockchain and cryptocurrencies, some challenges remain in Nigeria, including a lack of regulation and consumer protection, as well as a high degree of volatility in the cryptocurrency market. However, the government and regulators are beginning to show more interest in the technology and may develop clearer rules and regulations for its use.
Given its immense potential, blockchain and cryptocurrencies can play an important role in developing the Nigerian economy and providing financial inclusion for millions of Nigerians. However, it is important to conduct more research and educational programs to ensure that the public understands the risks and opportunities of these technologies and use them to benefit the country and its citizens.
.png)